What Is Hair Loss?
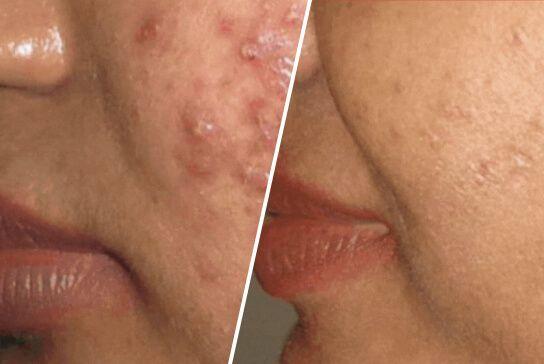
Hair loss, or alopecia, refers to the absence of hair growth on the scalp or body. It can result in hair fall of more than 150 strands every day. It affects men and women of all age groups and may vary in severity and form as it can be temporary or permanent and local or diffused.
Types of Hair Loss
Non-Scarring Alopecia: A type of hair loss that is reversible in the initial stages since the hair follicles remain undamaged, with multiple subtypes.
Androgenetic Alopecia: A genetic condition impacting 58% of Indian men and 25% of women between 30 and 50 years, leading to male pattern baldness or female pattern hair thinning if untreated.
Alopecia Areata: An autoimmune disorder causing patchy hair loss, which can advance to alopecia totalis (complete scalp hair loss) or alopecia universalis (loss of all body hair).
Telogen Effluvium: A temporary form of alopecia triggered by emotional stress, surgery, pregnancy, or illness, usually resolving within six months.
Causes of Hair Loss
Genetic Tendency: A family history of baldness raises the likelihood of androgen-driven scalp hair loss after puberty in both men and women.
Hormonal Imbalance: Hair loss can result from hormonal issues like PCOS, thyroid dysfunction, or insulin resistance, while pregnancy, childbirth, menopause, and prolonged birth control use may also trigger sudden hair loss in women.
Aging: Involutional hair loss refers to the aging-related slowdown of hair growth that leads to hair thinning and receding hairline.
Stress: High stress levels due to an emotional setback, surgery, including a hysterectomy, or chronic illness can trigger temporary hair loss.
Scalp Conditions: Psoriasis and fungal infections may affect your scalp health and result in hair loss.
Nutritional Deficiency: Hair loss may be a sign of underlying iron, zinc, biotin, or protein deficiency.
Signs of Hair Loss
Losing more than 120-150 hair strands daily
Hair thinning
Increased scalp visibility
Reduced hair growth
Scalp itching and inflammation
Receding or M-shaped hairline in men
Widening of the gap in women
Appearance of bald spots
If you note the above signs and symptoms of hair loss try and seek immediate medical attention to prevent permanent balding.


Hair Loss Treatments
1. Mesotherapy: During this minimally invasive hair loss treatment, dermatologists inject medicines and vitamins directly into the middle layer of the scalp, or mesoderm. Mesotherapy for alopecia delivers the medicines directly into the hair follicles to boost hair growth. It has a high patient satisfaction rate with minimal side effects.

2. (PRP) Platelet-rich Plasma Therapy: This non-surgical treatment can effectively reverse the early stages of male and female pattern baldness within limited sessions. Dermatologists inject autologous platelet-rich plasma into the bald patches to activate dormant hair follicles. This helps reduce hair fall and hair thinning, improve hair volume and density, and promote natural hair growth.
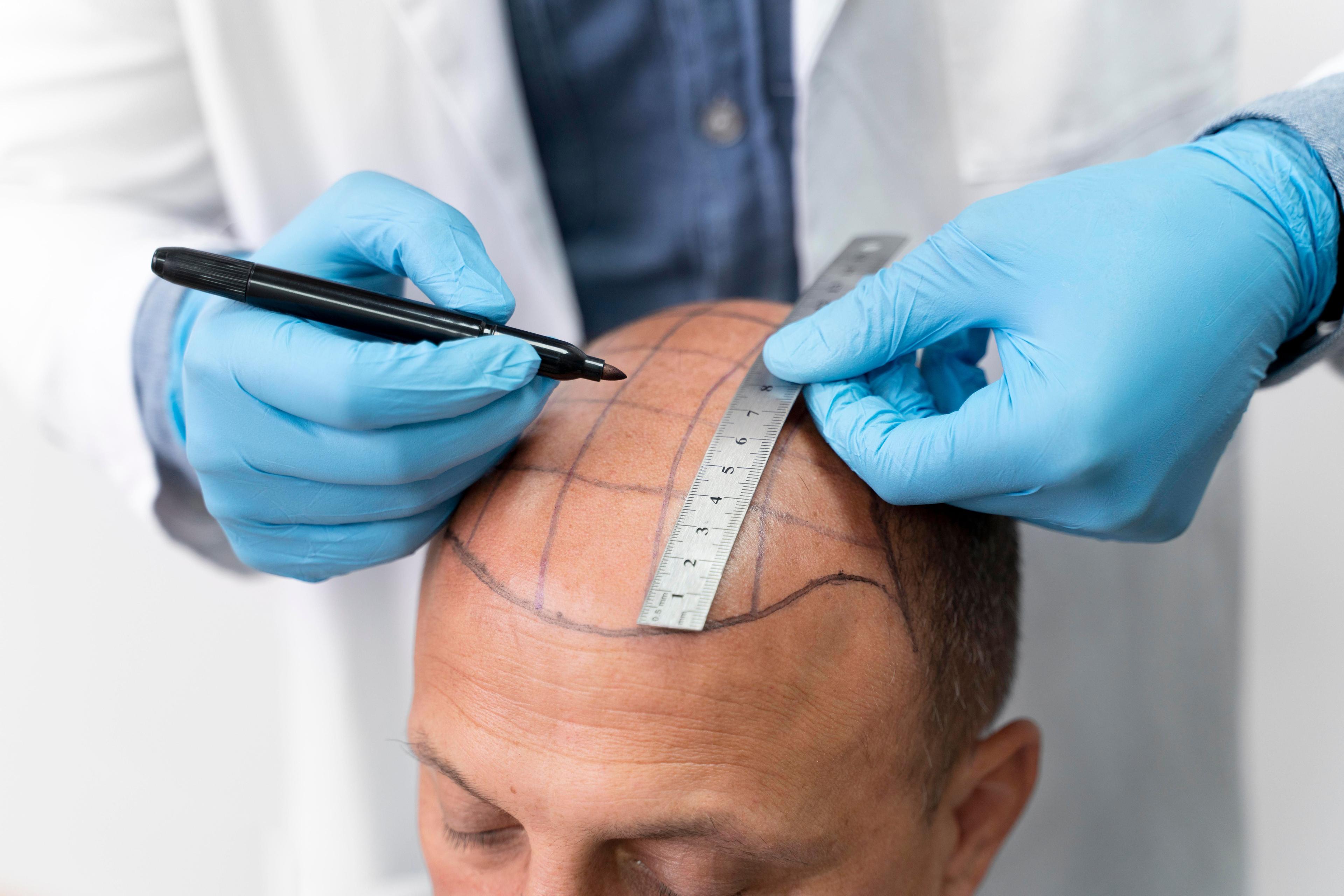
3. Hair Transplant Surgery: Dermatologists may recommend hair transplant surgery if you have irreversible hair loss due to the complete miniaturisation of follicles. During this surgical procedure, dermatologists graft healthy hair follicles in the balding-affected areas of the scalp.
Besides the above, your dermatologist may recommend a diet for healthy hair and a customised hair care regimen that includes the best hair fall control shampoo. Now you know all about hair loss types, causes, prevention tips, and dermatologist-recommended hair fall treatments. So, go ahead and make an informed decision if you are experiencing hair thinning. Click here to consult our top dermatologists if you are looking for the best hair doctor near you now!
Stay tuned for more hair care tips and treatment info!